How Pharmacogenomics is Revolutionizing Personalized Medicine
In recent years, the field of personalized medicine has been making headlines for its potential to transform healthcare. At the heart of this revolution is pharmacogenomics, a cutting-edge discipline that merges pharmacology and genomics to tailor medical treatments to individual genetic profiles. This innovative approach is not only enhancing the efficacy of treatments but also minimizing adverse effects, heralding a new era of precision in medicine.
What is Pharmacogenomics (,fär-mə-kō-jē-’nō-miks) (PGx)?
Pharmacogenomics (PGx) examines how an individual’s genetic makeup influences their response to drugs. By analyzing variations in genes that affect drug metabolism, efficacy and toxicity, PGx aims to customize drug therapy to the genetic profile of each patient. This contrasts sharply with the traditional one-size-fits-all approach, which often relies on population averages and can lead to variable outcomes and unintended side effects.
The Science Behind Pharmacogenomics
The effectiveness of medications can be influenced by genetic variations in several key areas:
- Drug Metabolism: The body’s ability to break down drugs is largely determined by genes encoding liver enzymes. Variations in these genes can lead to faster or slower drug metabolism, affecting drug levels in the body. For example, individuals with specific genetic variants might metabolize certain drugs too quickly, leading to suboptimal therapeutic levels, or too slowly, causing potentially dangerous side effects. Drug metabolism can also be affected by how different medications interact with each other once inside the body.
- Drug Transport: Genetic differences can affect drug transporters, proteins that move drugs into and out of cells. Variants in these transporters can influence how much of a drug reaches its target and how quickly it is cleared from the body.
- Drug Targets: Genetic variations can also alter the structure of drug targets, such as receptors or enzymes, impacting how well a drug works. For instance, patients with HER2-positive breast cancer are treated with trastuzumab, a therapy that specifically targets the HER2 protein. Sometimes, drug targets can be identified by analyzing biomarkers or messengers inside the body that are activated in different types of diseases. When multiple biomarkers are associated with one particular disease, biomarker analysis can be helpful in targeting the specific factors driving disease in an individual patient.
- Adverse Drug Reactions: Certain genetic profiles are associated with an increased risk of adverse drug reactions. For example, genetic testing can identify individuals at risk for severe reactions to drugs like carbamazepine, used to treat epilepsy, thus allowing for alternative treatments to be prescribed.
The Clinical Impact of Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics is revolutionizing personalized medicine by making treatments more precise and effective. Here’s how it’s making an impact:
- Enhanced Drug Efficacy: By tailoring drug prescriptions to genetic profiles, pharmacogenomics can significantly enhance the efficacy of treatments. For example, in oncology, genetic testing helps in selecting the most appropriate targeted therapies for cancer patients, improving response rates and survival outcomes. Enhanced efficacy can also save time by pointing clinicians towards the most effective treatment for an individual after a given diagnosis based on their genetics compared to a one size fits all approach that is currently commonplace and often delays time to healing when not precisely based on the individual patient’s needs.
- Reduced Adverse Drug Reactions: Genetic testing can identify individuals at higher risk for adverse drug reactions, allowing healthcare providers to choose safer medications or adjust dosages. This proactive approach not only improves patient safety but also reduces healthcare costs associated with managing drug-related complications.
- Optimized Drug Dosing: Personalized dosing based on genetic information ensures that patients receive the most effective dose of medication, minimizing the trial-and-error process and reducing the risk of underdosing or overdosing.
- Improved Drug Development: Pharmacogenomics is also shaping the future of drug development. By understanding how genetic variations affect drug responses, pharmaceutical companies can design more effective drugs with fewer side effects, and conduct more targeted clinical trials.
Real-World Applications and Examples
Several successful applications of pharmacogenomics highlight its transformative potential:
- Cardiovascular Medicine: Genetic testing for variations in the gene CYP2C19 can guide the use of clopidogrel, a drug used to prevent heart attacks and strokes. Individuals with certain genetic variants may not benefit from standard doses and may require alternative medications or adjusted doses.
- Psychiatry: In psychiatry and mental health, PGx testing can help tailor antidepressant therapy. For example, genetic tests can predict how well a patient will respond to medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), helping to avoid ineffective treatments and reduce side effects.
- Oncology: In cancer treatment, the identification of genetic mutations in tumors can guide the use of targeted therapies. For instance, patients with HER2-positive breast cancer are treated with trastuzumab, a targeted therapy that specifically addresses the HER2 protein.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its promising benefits, pharmacogenomics faces several challenges. These include the high cost of genetic testing, the need for more extensive research to understand the full range of genetic variations, and the integration of pharmacogenomic data into routine clinical practice. Additionally, there are ethical and privacy concerns regarding genetic information that need to be addressed. Additionally, adoption by physicians is essential for advancing this important testing, as their support and use of pharmacogenomic tools in patient care will be key to driving innovation and making these personalized treatments more accessible.
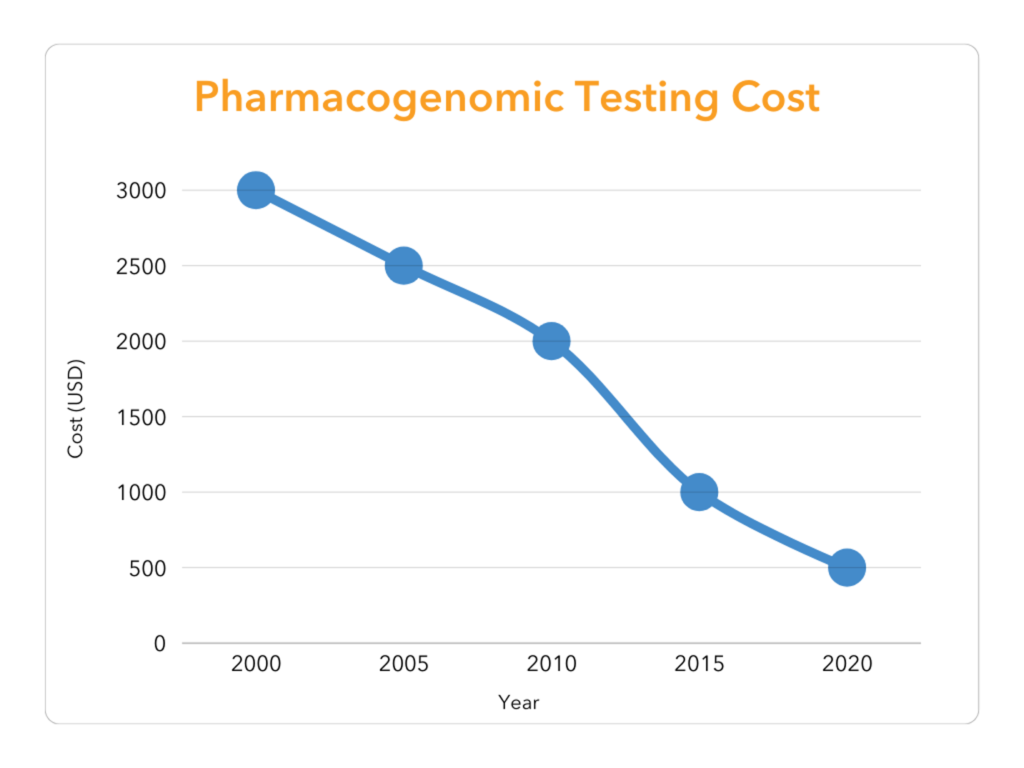
Looking ahead, the future of pharmacogenomics is extremely bright. Advances in genomic technology and decreasing costs of genetic testing are expected to make pharmacogenomic insights more accessible. As more data becomes available and our understanding of genetics deepens, personalized medicine will become increasingly precise and widespread, revolutionizing treatments and improving patient outcomes. As more physicians adopt pharmacogenomics testing, there will be increased demand and broader acceptance for future developments in this cutting-edge field. AffirmedRx is committed to enhancing patient care through a streamlined, personalized approach to our pharmacogenomics clinical program and looks forward to implementing this elevated healthcare service offering for our clients.
Conclusion
Pharmacogenomics is at the forefront of the personalized medicine revolution, offering the promise of tailored treatments that are both more effective and safer. By harnessing the power of genetic information, pharmacogenomics is paving the way for a future where medical care is customized to individual needs, marking a significant leap forward in the quest for precision healthcare. As this field continues to evolve, it holds the potential to transform not only how we treat diseases but also how we understand and approach health and wellness. AffirmedRx is committed to bringing you advancements in this industry as they arrive; contact us today to learn more about our innovative ARx Elevate Pharmacogenomics programs for your members!

